Notes
Chapter 9: Fundamental Physics
Section 2: The Notion of Reversibility https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-2--the-notion-of-reversibility
https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-2--the-notion-of-reversibility
Testing for reversibility [in cellular automata]
Numbers of reversible [cellular automaton] rules
Inverse [cellular automaton] rules
Surjectivity and injectivity [in cellular automata]
Directional reversibility [in cellular automata]
Second-order cellular automata
History [of second-order cellular automata]
Properties [of second-order cellular automata]
Properties [of second-order cellular automata]
Generalized additive [cellular automaton] rules
Section 3: Irreversibility and the Second Law of Thermodynamics https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-3--irreversibility-and-the-second-law-of-thermodynamics
https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-3--irreversibility-and-the-second-law-of-thermodynamics
Current thinking on the Second Law
My explanation of the Second Law
Biological systems and Maxwell's demon
Section 4: Conserved Quantities and Continuum Phenomena https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-4--conserved-quantities-and-continuum-phenomena
https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-4--conserved-quantities-and-continuum-phenomena
[Conserved quantities in] physics
Implementation [of conserved quantity test]
More general conserved quantities
[Conserved quantities in] PDEs
Limiting procedures [for cellular automata]
PDE approximations [to cellular automata]
Section 5: Ultimate Models for the Universe https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-5--ultimate-models-for-the-universe
https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-5--ultimate-models-for-the-universe
History of ultimate models [of physics]
Theological implications [of ultimate models of physics]
[History of] origins of physical models
Simplicity in scientific models
Mechanistic models [in physics]
Initial conditions [for the universe]
Section 6: The Nature of Space https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-6--the-nature-of-space
https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-6--the-nature-of-space
Section 7: Space as a Network https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-7--space-as-a-network
https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-7--space-as-a-network
Generalizations [of trivalent networks]
Maintaining simple rules [for networks]
Continuum limits [of networks]
Implementation [of network properties]
Finding layouts [for networks]
Section 8: The Relationship of Space and Time https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-8--the-relationship-of-space-and-time
https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-8--the-relationship-of-space-and-time
Section 9: Time and Causal Networks https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-9--time-and-causal-networks
https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-9--time-and-causal-networks
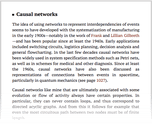
Implementation [of causal networks]
[Causal networks for] mobile automata
Section 10: The Sequencing of Events in the Universe https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-10--the-sequencing-of-events-in-the-universe
https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-10--the-sequencing-of-events-in-the-universe
Implementation [of generalized substitution systems]
The sequential limit [in generalized substitution systems]
[Generalized substitution system] rule (b)
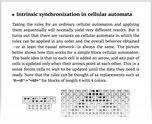
Intrinsic synchronization in cellular automata
Section 11: Uniqueness and Branching in Time https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-11--uniqueness-and-branching-in-time
https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-11--uniqueness-and-branching-in-time
Spacetime networks from multiway systems
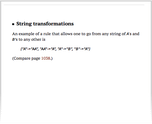
Commuting operations [on strings]
Conditions for convergence [in string rewriting]
Confluence [in string rewriting]
Section 12: Evolution of Networks https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-12--evolution-of-networks
https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-12--evolution-of-networks
Neighbor-independent [network substitution] rules
Implementation [of network substitution rules]
Identifying subnetworks [in networks]
Number of [possible network] replacements
[Generating] arbitrary transformations [between networks]
[Networks generated by] random replacements
Cellular structures [in nature]
Non-overlapping [network] clusters
1- and 2-connection [network] clusters
Reversibility [of networks and universe]
Feynman diagrams [and networks]
Chemical analogy [for network substitutions]
Section 13: Space, Time and Relativity https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-13--space-time-and-relativity
https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-13--space-time-and-relativity
Section 14: Elementary Particles https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-14--elementary-particles
https://www.wolframscience.com/nks/chap-9--fundamental-physics--notes#sect-9-14--elementary-particles
Types of [elementary] particles
History [of elementary particles]
![Testing for reversibility [in cellular automata] Testing for reversibility [in cellular automata]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-2--testing-for-reversibility-in-cellular-automata--textonly.png)
![Numbers of reversible [cellular automaton] rules Numbers of reversible [cellular automaton] rules](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-2--numbers-of-reversible-cellular-automaton-rules--textonly.png)
![Inverse [cellular automaton] rules Inverse [cellular automaton] rules](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-2--inverse-cellular-automaton-rules--textonly.png)
![Surjectivity and injectivity [in cellular automata] Surjectivity and injectivity [in cellular automata]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-2--surjectivity-and-injectivity-in-cellular-automata--textonly.png)
![Directional reversibility [in cellular automata] Directional reversibility [in cellular automata]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-2--directional-reversibility-in-cellular-automata--textonly.png)

![History [of second-order cellular automata] History [of second-order cellular automata]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-2--history-of-second-order-cellular-automata--textonly.png)
![Properties [of second-order cellular automata] Properties [of second-order cellular automata]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-2--properties-of-second-order-cellular-automata-1--textonly.png)
![Properties [of second-order cellular automata] Properties [of second-order cellular automata]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-2--properties-of-second-order-cellular-automata-2--textonly.png)
![Generalized additive [cellular automaton] rules Generalized additive [cellular automaton] rules](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-2--generalized-additive-cellular-automaton-rules--textonly.png)













![[Conserved quantities in] physics [Conserved quantities in] physics](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-4--conserved-quantities-in-physics--textonly.png)
![Implementation [of conserved quantity test] Implementation [of conserved quantity test]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-4--implementation-of-conserved-quantity-test--textonly.png)


![[Conserved quantities in] PDEs [Conserved quantities in] PDEs](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-4--conserved-quantities-in-pdes--textonly.png)


![Block rules [examples] Block rules [examples]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-4--block-rules-examples--textonly.png)
![Limiting procedures [for cellular automata] Limiting procedures [for cellular automata]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-4--limiting-procedures-for-cellular-automata--textonly.png)
![PDE approximations [to cellular automata] PDE approximations [to cellular automata]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-4--pde-approximations-to-cellular-automata--textonly.png)




![History of ultimate models [of physics] History of ultimate models [of physics]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-5--history-of-ultimate-models-of-physics--textonly.png)
![Theological implications [of ultimate models of physics] Theological implications [of ultimate models of physics]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-5--theological-implications-of-ultimate-models-of-physics--textonly.png)
![[History of] origins of physical models [History of] origins of physical models](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-5--history-of-origins-of-physical-models--textonly.png)


![Apparent simplicity [of laws] Apparent simplicity [of laws]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-5--apparent-simplicity-of-laws--textonly.png)
![Mechanistic models [in physics] Mechanistic models [in physics]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-5--mechanistic-models-in-physics--textonly.png)


![Initial conditions [for the universe] Initial conditions [for the universe]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-5--initial-conditions-for-the-universe--textonly.png)
![Consequences of an ultimate model [of physics] Consequences of an ultimate model [of physics]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-5--consequences-of-an-ultimate-model-of-physics--textonly.png)

![History of discrete [models of] space History of discrete [models of] space](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-6--history-of-discrete-models-of-space--textonly.png)

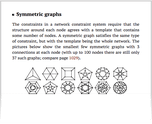
![Symmetry [of discrete space] Symmetry [of discrete space]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-6--symmetry-of-discrete-space--textonly.png)



![Generalizations [of trivalent networks] Generalizations [of trivalent networks]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-7--generalizations-of-trivalent-networks--textonly.png)
![Maintaining simple rules [for networks] Maintaining simple rules [for networks]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-7--maintaining-simple-rules-for-networks--textonly.png)

![Continuum limits [of networks] Continuum limits [of networks]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-7--continuum-limits-of-networks--textonly.png)


![Counting of [network] nodes Counting of [network] nodes](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-7--counting-of-network-nodes--textonly.png)
![Cycle lengths [in networks] Cycle lengths [in networks]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-7--cycle-lengths-in-networks--textonly.png)
![Implementation [of network properties] Implementation [of network properties]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-7--implementation-of-network-properties--textonly.png)
![Finding layouts [for networks] Finding layouts [for networks]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-7--finding-layouts-for-networks--textonly.png)
![Hamming distances [in networks] Hamming distances [in networks]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-7--hamming-distances-in-networks--textonly.png)
![Continuous mathematics [and networks] Continuous mathematics [and networks]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-7--continuous-mathematics-and-networks--textonly.png)
![History [of views of time] History [of views of time]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-8--history-of-views-of-time--textonly.png)




![Implementation [of causal networks] Implementation [of causal networks]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-9--implementation-of-causal-networks--textonly.png)
![[Causal networks for] mobile automata [Causal networks for] mobile automata](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-9--causal-networks-for-mobile-automata--textonly.png)
![Computational compression [and time] Computational compression [and time]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-9--computational-compression-and-time--textonly.png)
![[Causal networks for] 2D mobile automata [Causal networks for] 2D mobile automata](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-9--causal-networks-for-2d-mobile-automata--textonly.png)
![Implementation [of generalized substitution systems] Implementation [of generalized substitution systems]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-10--implementation-of-generalized-substitution-systems--textonly.png)

![The sequential limit [in generalized substitution systems] The sequential limit [in generalized substitution systems]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-10--the-sequential-limit-in-generalized-substitution-systems--textonly.png)
![[Generalized substitution system] rule (b) [Generalized substitution system] rule (b)](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-10--generalized-substitution-system-rule-b--textonly.png)








![Commuting operations [on strings] Commuting operations [on strings]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-11--commuting-operations-on-strings--textonly.png)
![Conditions for convergence [in string rewriting] Conditions for convergence [in string rewriting]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-11--conditions-for-convergence-in-string-rewriting--textonly.png)
![Confluence [in string rewriting] Confluence [in string rewriting]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-11--confluence-in-string-rewriting--textonly.png)
![Completion [in multiway systems] Completion [in multiway systems]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-11--completion-in-multiway-systems--textonly.png)

![Neighbor-independent [network substitution] rules Neighbor-independent [network substitution] rules](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-12--neighbor-independent-network-substitution-rules--textonly.png)
![Implementation [of network substitution rules] Implementation [of network substitution rules]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-12--implementation-of-network-substitution-rules--textonly.png)
![Identifying subnetworks [in networks] Identifying subnetworks [in networks]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-12--identifying-subnetworks-in-networks--textonly.png)
![Number of [possible network] replacements Number of [possible network] replacements](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-12--number-of-possible-network-replacements--textonly.png)

![[Generating] arbitrary transformations [between networks] [Generating] arbitrary transformations [between networks]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-12--generating-arbitrary-transformations-between-networks--textonly.png)
![[Generating] random networks [Generating] random networks](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-12--generating-random-networks--textonly.png)
![[Networks generated by] random replacements [Networks generated by] random replacements](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-12--networks-generated-by-random-replacements--textonly.png)
![Cellular structures [in nature] Cellular structures [in nature]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-12--cellular-structures-in-nature--textonly.png)
![[Network] cluster numbers [Network] cluster numbers](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-12--network-cluster-numbers--textonly.png)
![Non-overlapping [network] clusters Non-overlapping [network] clusters](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-12--non-overlapping-network-clusters--textonly.png)
![1- and 2-connection [network] clusters 1- and 2-connection [network] clusters](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-12--1-and-2-connection-network-clusters--textonly.png)
![Connectedness [of universe] Connectedness [of universe]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-12--connectedness-of-universe--textonly.png)
![Reversibility [of networks and universe] Reversibility [of networks and universe]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-12--reversibility-of-networks-and-universe--textonly.png)
![Feynman diagrams [and networks] Feynman diagrams [and networks]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-12--feynman-diagrams-and-networks--textonly.png)
![Chemical analogy [for network substitutions] Chemical analogy [for network substitutions]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-12--chemical-analogy-for-network-substitutions--textonly.png)
![Symbolic representations [and networks] Symbolic representations [and networks]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-12--symbolic-representations-and-networks--textonly.png)





![Standard treatment [of relativity] Standard treatment [of relativity]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-13--standard-treatment-of-relativity--textonly.png)

![Particle physics [and relativity] Particle physics [and relativity]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-13--particle-physics-and-relativity--textonly.png)

![Types of [elementary] particles Types of [elementary] particles](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-14--types-of-elementary-particles--textonly.png)
![History [of elementary particles] History [of elementary particles]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-14--history-of-elementary-particles--textonly.png)


![Identifying particles [in networks] Identifying particles [in networks]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-14--identifying-particles-in-networks--textonly.png)

![Spin [of particles] Spin [of particles]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-14--spin-of-particles--textonly.png)

![More particles [in physics] More particles [in physics]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-14--more-particles-in-physics--textonly.png)
![History [of gravity theory] History [of gravity theory]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-15--history-of-gravity-theory--textonly.png)






![[Properties of] discrete spaces [Properties of] discrete spaces](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-15--properties-of-discrete-spaces--textonly.png)
![Manifold [properties and] undecidability Manifold [properties and] undecidability](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-15--manifold-properties-and-undecidability--textonly.png)





![Pure gravity [theory] Pure gravity [theory]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-15--pure-gravity-theory--textonly.png)


![History [of quantum theory] History [of quantum theory]](/nks/img/thumbnails/notes-9-16--history-of-quantum-theory--textonly.png)